sikak
By Thorncombe Street
© Copyright Colin Smith and licensed for reuse under this Creative Commons Licence.
話はがらりと変わりますが、日本ではVPPがリバイバルの様相を見せているようですね。
仮想発電所(Virtual Power Plant:VPP)という言葉を初めて耳にしたのは10年以上前だった気がします。 当時は、工場などにあるディーゼルエンジンの自家発電機(自家発)を遠隔制御し、そうしてできた各工場の余剰電力を束ねてあたかも1つの発電所のように使うというものだったと記憶しています。
VPPというのは、そのような複数の地点で配電網に接続されている、系統から見るといわゆる分散型の中・小型電源を束ねて、あたかも1つの発電所のように取り扱う概念ということができます。 当時は、ほぼ、分散型の電源=自家発と捉えられていたと思うのですが、時が経って、風力発電や太陽光発電などの再生可能エネルギー発電施設やビル・住宅に設置された蓄電池や燃料電池、更には、弊ブログで取り上げてきた、工場やビル・住宅が提供するDR資源も分散型の電源として、VPPの取り扱い対象に加わってきたようです。DRアグリゲータというのも、DR資源に特化した分散型の電源を束ねて取り扱うVPPと考えることができる-という訳です。
そのような、最近の状況を反映したVPPの定義はどうなっているのか、本日は、VPPの定義について、考えてみたいと思います。
まず、インターネット検索で見つけた、米国エネルギー省が4年ごとに発行する2015年版の技術レビュー、もう1つは2010年の少し古いレポートですが欧州委員会のスマートグリッドタスクフォースの最終報告書、もう1つは、Pike Research(現、Navigant)Peter Asmus氏のVPPの定義とVPP市場の予測、最後に、GTMリサーチの、システム面から見たVPPの定義です。
では、はじめます。
■ 米国におけるVPPの定義
US DOE Quadrennial Technology Review 2015
Chapter 3: Enabling Modernization of the Electric Power System3D Flexible and Distributed Energy Resources
A virtual power plant is an operating concept where a group of DERs that are geographically disperse (e.g., associated with different utility meters, residing on different feeders, or not having clearly defined electrical boundaries) is aggregated and coordinated to act as a single entity. This technology concept can include any combination of individual grid-enabled customer resources (e.g., distributed generation, electric vehicles, and energy storage) or integrated resources (e.g., smart buildings and microgrids). Additionally, the control of the aggregated resources is accomplished through a mix of strategies and signals that can involve markets. The concept of virtual power plants is shown in Figure 3.D.7.
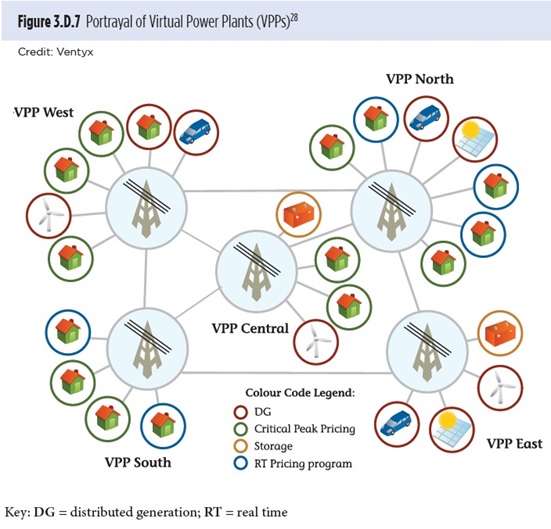
Major challenges to implementing this technology effectively include the need for good understanding of the physical topology and connectivity of the various systems where the resources are located and broad visibility to observe the state of various components and assets. <途中省略>Aggregated demand response is a subset of this concept. <途中省略> The aggregated resource can bid into wholesale electricity markets and provide other grid services if allowed.
ザッと訳します。
VPPとは、地理的に分散し、個別の電力計で発電量が計測され、場合によっては異なる給電線に接続されている「分散型の電源」の出力を束ねて一つの発電所のように運用する技術概念である。ここで、「分散型の電源」には、系統側から制御可能な需要家資源として、一般家庭に設置された太陽光パネルなどの再生可能エネルギー設備、負荷調整で生み出すDR資源、電気自動車や蓄電池、更に、スマートビルやマイクログリッドから提供される統合された資源を含む。そして、VPPの出力は、通常の発電機同様、外部からの給電指令に従う以外に、電力市場取引結果に合わせる場合、価格反応型DRのように、需要家側の意志・嗜好に依存するものもある。DR資源を束ねるDRアグリゲーションは、VPPの1形態と捉えることができる。
仮想発電所の概念を示す図3.D.7に関しての説明はありませんでしたが、VPP Southは、CPP(緑の円)およびRTP(青の円)の2種類の価格反応型DRプログラムでDR資源を束ねるDRアグリゲータのようです。それに対してVPP Eastは、想像するに、再生可能エネルギー設備と電気自動車(赤の円)と蓄電池(橙色の円)を「分散型の電源」とし、再生可能エネルギーの出力変動を蓄電池で吸収して仮想発電所として電力提供するのでしょう。VPP Central、VPP NorthとVPP Westは、取り扱う「分散型の電源」としてVPP SouthとVPP Eastを合わせたものをとり扱っており、より高度なDERMSを用いて、トータル出力を制御しているのでしょうね。
■ 欧州におけるVPPの定義
EU Commission Task Force for Smart Grids
Expert Group 1: Functionalities of smart grids and smart meters
Final Deliverable (December 2010)
Virtual Power Plant – VPP
A Virtual Power Plant (VPP) aggregates the capacity of many diverse Distributed Energy Resources (DER), it creates a single operating profile from a composite of the parameters characterizing each DER and can incorporate the impact of the network on aggregate DER output. There are two types of VPP, the Commercial VPP (CVPP) and the Technical VPP (TVPP).
Commercial VPP
A CVPP has an aggregated profile and output which represents the cost and operating characteristics for the DER portfolio. The impact of the distribution network is not considered in the aggregated CVPP profile.
Services/functions from a CVPP include trading in the wholesale energy market, balancing of trading portfolios and provision of services (through submission of bids and offers) to the system operator. The operator of a CVPP can be any third party aggregator or a Balancing Responsible Party (BRP) with market access; e.g. an energy supplier.
Technical VPP
The TVPP consists of DER´s placed in the same distribution network region. The TVPP includes the real-time influence of the local network on DER aggregated profile as well as representing the cost and operating characteristics of the portfolio. Services and functions from a TVPP include local system management for Distribution System Operator (DSO), as well as providing Transmission System Operator (TSO) system balancing and ancillary services. The operator of a TVPP requires detailed information on the local network.
こちらのVPPの定義部分もザッと訳すと、こんな感じでしょうか?
仮想発電所(Virtual Power Plant:VPP)
VPPは、多くの様々な分散エネルギー資源(Distributed Energy Resources:DER)を束ねて運用することで、個々のDERの長所を活かし短所を補って、全体として大規模発電所に匹敵するような出力を得たり、系統にもたらされる悪影響を緩和したりする仕組みである。 VPPには、コマーシャルVPP(CVPP)とテクニカルVPP(TVPP)の2つの種類がある。
コマーシャルVPP(Commercial VPP:CVPP)
CVPPは、「分散型の電源」を束ねて電力卸売市場で売買取引を行ない、入札価格で決定した市場取引結果に応じて系統に電力供給を行なうもので、CVPPが束ねて提供する「分散型の電源」の配電網に対する影響は考慮されない。自らは発電所を保有しないアグリゲータ、電力トレーダー、電力ブローカー、需給バランス責任者(Balancing Responsible Party:BRP)が、CVPPとして電力取引市場を介して電力供給を行なう。
テクニカルVPP(Technical VPP:TVPP)
TVPPでは、提供する「電源」の系統へのリアルタイムの影響が考慮され、同じ配電網に電力供給可能な「分散電源」から構成される。 TVPPは、所属する配電網の系統運用に寄与するだけでなく、上位の送電事業者の需給バランスにも貢献し、アンシラリーサービスを提供することがきる。
■ Pike Research Peter Asmus氏のVPPの定義とVPP市場の予測
Microgrids, Virtual Power Plants and Our Distributed Energy Future
III. Definition: Virtual Power Plant
Virtual power plants – a term frequently used interchangeably with ‘‘microgrids’’ – rely upon software systems to remotely and automatically dispatch and optimize generation or demand side or storage resources in a single, secure Web-connected system. In short, VPPs represent an ‘‘Internet of energy,’’ tapping existing grid networks to tailor electricity supply and demand services for a customer, maximizing value for both end user and distribution utility through software innovations (Figure 2).
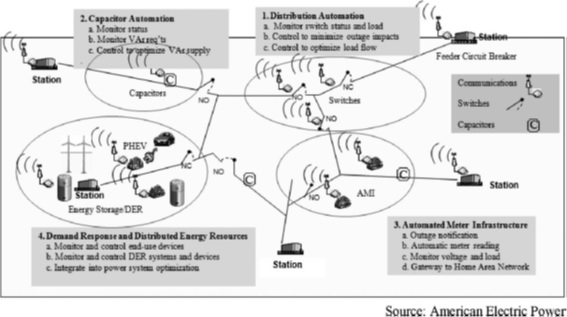
Figure 2: Diagram Displaying VPP Versatility
VPPは、1つのセキュアなWEB接続されたシステムで、分散電源や負荷や蓄電池を遠隔自動制御し運転の最適化を行なうものである。一言でいうと、VPPとはIoTのエネルギー版、すなわち、Internet of Energy(IoE)であり、Figure2に示したように、ソフトウェアイノベーションによって需要家側からの電力供給と需要家の負荷を制御することでエンドユーザと配電事業者双方にとっての価値を最大化しようとするものである。
VII. VPPs: Market Forecasts
Unlike microgrids, utilities will have to play a major role in the evolution of the VPP market. With its emphasis on smartmeters, realtime pricing, and demand response, the Smart Grid is actually a necessary prerequisite for VPPs. What distinguishes a VPP from the Smart Grid is that most VPPs (at least in the U.S.) attempt to create a mini-ISO on the customer side of the meter to optimize energy resource aggregation. VPPs are likely a natural evolution of the Smart Grid and are highly synergistic with the more sophisticated billing systems that are emerging as hallmarks of ‘‘backroom operations’’ supporting the rollout of the Smart Grid. Developing market forecasts for a nebulous technology category of ‘‘virtual power plants’’ is a daunting task. Competing definitions, temporary aggregations of highly divergent technologies, and resources that may only be tapped for minutes (or even seconds) at a time, all add up to complexity and uncertainty. A market forecast, published in fall 2010 by Pike Research, divides up the VPP universe into four distinct segments:
スマートメーター、リアルタイムプライシングとデマンドレスポンスのようなスマートグリッドの道具立ては、VPPを実現するために必要な手段にもなっている。そして、スマートグリッドの進展を後方支援する高度に洗練化された課金システムとの相乗作用で、VPPは、ここまで自然進化を遂げてきた。 「分散型の電源」としてまったく異なるテクノロジーの集合を対象としなければならなかったため、VPPの発展の過程で、特定の「分散型の電源」を対象としてきたVPPの定義の間で矛盾が生じ、VPPは、複雑で曖昧模糊とした捉え方にならざるを得なかった。 そこで、2010年秋発刊したPike Researchのレポートでは、VPPの世界を4つに分けて、その市場予測を試みている。
DR-based VPPs: This is the largest commercial segment in the U.S., since the U.S. has the most mature DR market in the world (Figure 4).
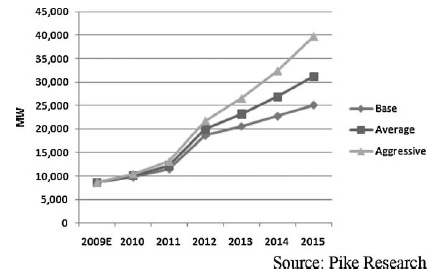
Figure 4: DR-VPP Capacity Worldwide, Base, Average and Aggressive Scenarios, 2009–2015
DRベースのVPP:米国ではDR市場が最も成熟しているため、Figure 4に示す通り、米国ではDRベースのVPPが最も商業的に成功している。
Supply-side VPPs: Europe, particularly Germany, has led the world in this category, though most of the projects have been R&D pilots, with only a handful of VPPs in commercial operation.
供給サイドVPP:欧州、特にドイツでは、このカテゴリのVPPがトップで、まだ実証段階のものも多いが、一握りの成功事例が既に存在する。
Mixed-asset VPPs: This is the ultimate goal of the VPP, bringing distributed generation and DR together, to provide a synergistic sharing of grid resources to squeeze out more value, thereby reducing capital costs. Few of these projects are in commercial operation today.
異種「分散型電源」の混合設備を用いたVPP:このタイプがVPPとしての最終目標で、再生可能エネルギーを含む分散電源とDRを併用することにより、そのシナジー効果によって、資本コストを低減すると同時に、より多くの価値を引き出そうとするものである。このタイプのVPPが、今日すでにいくつか商業運転中である。
Wholesale auction VPPs: Unique to Europe, VPP auctions have been used in Europe as a condition of mergers, requiring asset owners to auction off baseload and peaking capacity to bidders under short- and long term contracts. Unlike the category of supply-side VPP segments, these resources are typically traditional centralized power plants burning fossil fuels.
VPPオークション:欧州での慣行として、電力会社が合併する際、大規模合併によって電力卸売市場が寡占状態となり市場価格への悪影響が出ないよう、VPPの競売が合併の条件として広く使われている。これは合併で大きくなった発電設備容量の一部をVPP容量として競売にかけるもので、VPP容量を買う企業は電力設備を保有しているかのように電力供給を行う権利を得るものである。このVPPは、「分散型の電源」ではなく、他社の大規模電源(の一部)を自社電源のように用いることができるという意味で、仮想発電所ではあるが、今回のVPPとは趣を異にするものである。
Pike Research has developed market forecasts for each of these four segments. All told, the total current VPP capacity worldwide is 19,428 MW. The largest segment is wholesale auctions exclusively in Europe, but which represents 51 percent of the total VPP market. The next largest segment is the DR-based VPPs which dominate the U.S. market, with 44 percent of the total global capacity. The supply and mixed-asset segments split the remaining 5 percent of the VPP market virtually equally. The total revenue from VPPs worldwide is almost $5 billion, with the vast majority (90 percent) of that revenue stream captured by the wholesale auction VPP segment.
Over time, it is expected that many supply-side VPPs will morph into mixed-asset VPPs, as more cost-competitive storage enters the market and as DR resources continue to grow in terms of capacity and sophistication. Ultimately, the market for VPPs will likely undergo an evolution where the lines between the first three segments profiled will blur further.
パイクリサーチの調べによると、現在世界中で利用可能なVPP容量は19,428MWで、欧州で行われているVPPオークションがVPP市場の51%を占めている。米国のDRベースのVPPが次に多くて44%。供給サイドVPPと混合設備を用いたVPPは、合わせても5%に満たない。
収益面から見ると、差はもっと歴然としている。現在世界中で利用されているVPPの総収益は約50億ドルだが、VPPオークションが90%を占めている。
ただし、時間とともに、より価格競争力のある蓄電池が市場参入し、DR資源に関しても利用形態が洗練化されて成長し続け、多くの供給サイドVPPは混合設備型VPPに移行するものと予想される。 究極的には、VPPの市場は、最初の3つのタイプのVPPの境界線があいまいになっていく形で進化をたどるのではないかと思われる。
■ GTM Researchの考える分散電源管理システム(DERMS)とVPPの関連
Many utilities are starting with demand response DERMS projects to manage wind farms. Europe, in particular, has made significant headway and is ahead of the U.S. because of its higher penetration of renewable energy. France’s first virtual power plant, installed in 2011, is designed to manage demand response loads to balance wind power. As more solar and wind come on-line in certain regions of the U.S., intelligent storage and DERMS are expected to proliferate. <途中省略>
Storage is becoming cost-competitive in California and New York, where demand charges are high and frequency regulation markets value storage. DERMS platforms will be increasingly important for utilities operating in these markets where solar and storage are coming together. “Though these systems vary in complexity and even function,” said Saadeh, “vendor opportunities lie in the ability to aggregate smaller customers, enable system-wide ancillary support, increase market participation and mitigate generation intermittency.”
VPPという技術概念の実装にあたって利用されるソフトウエア基盤が、分散エネルギー資源管理システム(Distributed Energy Resource Management System:DERMS)である。
多くの電力会社は、風力発電所を管理するためにDRを利用したDERMSのプロジェクトを立ち上げている。この分野では、再生可能エネルギーの利用が進んでいる欧州が米国に先行しており、 フランスでは、風力発電の出力変動を、DRを用いてバランスさせようとする最初のVPPが2011年に運用を開始している。
米国の特定の地域では、太陽光発電や風力発電が大量に系統接続されることが予定されているので、インテリジェントな蓄電池とDERMSの増設が検討されている。
電気料金が高く、周波数調整市場価格の高いカリフォルニア州とニューヨーク州では、すでに蓄電池は、他の電源と価格競争できるようになっている。 今後、その他の州でも、太陽光発電と蓄電池が入ってくるので、DERMSプラットホームが重要となってくるだろう。現時点では、DERMSとして提供されているシステムの複雑さ、機能はまちまちだが、今後は小口需要家の分散型の電源を束ねて系統大のアンシラリーサービスをサポートできるとともに、系統に流入する再生可能エネルギーの出力変動に対応するような機能が求められるだろう。
本日は、ここまでです。
- VPPというのは、地理的に分散し、個別の電力計で発電量が計測され、場合によっては異なる給電線に接続されている「分散型の電源」の出力を束ねて一つの発電所のように運用する技術概念である。
- VPPをシステムとして実装する際、そのソフトウェア基盤となるものがDERMSである。
- DR資源は、VPPに利用される「分散型の電源」の1つであり、DRアグリゲータが利用しているシステムもVPPのシステムということができる。
ということをご理解いただけたでしょうか?
下図は、「European Utility Week 2015」でSchneider Electric社のプレゼン資料として入手したものですが、Pike ResearchのVPPの分類であるDG-VPP、DR-VPPおよびMixed Asset-VPPが示されています。
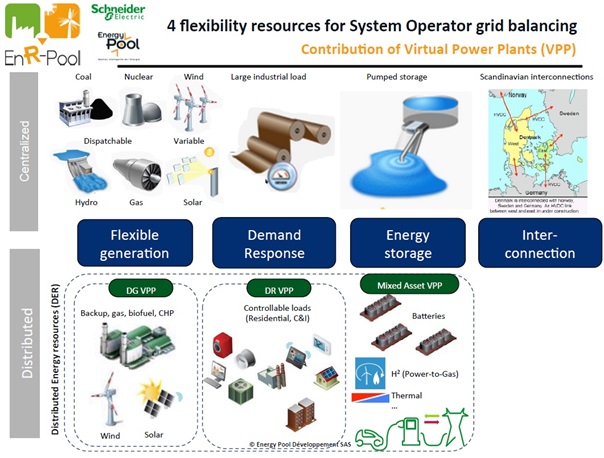
EnergyPoolのソリューションは、すでにMixed Asset-VPPまでを考慮したものになっているということでしょうか。
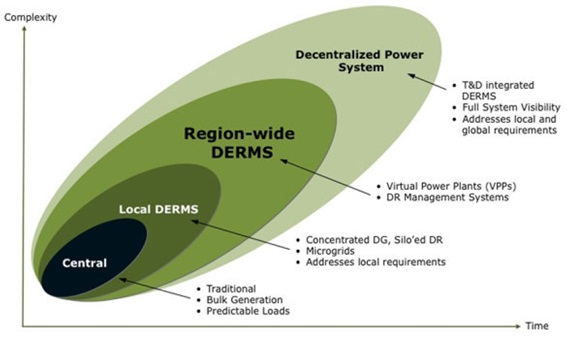
さて、最後のGTMリサーチの絵に関しては特に説明はなかったのですが、明らかにGTMリサーチが考える電力系統制御システムの将来像を示唆しているものと思われます。
グラフ右下で黒の楕円(Central)で示されているのが、従来の(Traditional)大型発電所(Bulk Generation)を用いて需要予測(Predictable Loas)を基に作成した発電計画に基づく運用ですね。 これに対して、
これまで日本でもスマートシティ実証で実施されていたのは、Local DERMSレベルで、MicrogridやSilo’ed DR、すなわち特定の独立したDRプログラムでローカルな要求に応えよう(Addresses local requirements)というものでした。
VPPは、次のRegional-wide DERMSレベルとされており、DRプログラムも異種・複数のものを同時に扱えることを意味するのでしょうか、DR Management Systemsとなっています。
そして究極の電力系統制御システムがDecentralized Power Systemで、送配電の境がなく(T&D integrated DERMS)系統全体が見渡せて(Full System Visibility)、その分散型電力系統システムでローカルな課題から系統大の課題に対応できる(Addresses local and global requirements)と考えられているようです。これがスマートグリッドの最終形ということだと思うのですが、自分が抱いていたスマートグリッドに対するイメージと非常に近いもので、気分を良くしています。
次回は、新しく始めたブログのタイトルにもあるVPPとエネルギーリソースアグリゲーションの関係について考えたいと思います。
終わり
- 投稿タグ
- Demand Response, DER, DERMS, Smart Grid, VPP, エネルギーリソースアグリゲーション, スマートグリッド, デマンドレスポンス, 仮想発電所, 分散型電源


Pingback: VPPとエネルギーリソースアグリゲーション-その5 | 仮想発電所 | インターテックリサーチ株式会社
Pingback: VPPとエネルギーリソースアグリゲーション-その5 | 仮想発電所 | インターテックリサーチ株式会社
Pingback: エネルギー事業者・自治体産業部局必読! これからのエネルギー事業の羅針盤となるブログ3選 | 2032年の世界を東京から考えるblog